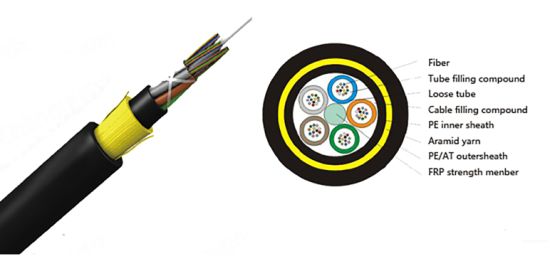
The fiber optic cable adopts a loose-layer twisted structure, and the optical fiber is sheathed in a loose tube made of high-modulus polyester material, and the tube is filled with a waterproof compound. The loose tube (and filler rope) is twisted around a non-metallic central reinforcement (FRP) into a compact cable core, and the gaps in the cable core are filled with water blocking grease. The inner sheath of polyethylene (PE) is extruded outside the cable core, and then two layers of aramid yarns for strengthening are twisted in both directions, and finally a polyethylene (PE) jacket or an anti-corrosion (AT) jacket is extruded.
Description of raw materials of ADSS cable:
1. Central reinforcement core: high-strength FRP fiber, with anti-tensile, anti-interference and anti-corrosion functions, to ensure that the operating window is higher than the national standard.
2. Optical fiber: YOFC, Fiberhome or Corning’s national standard A-level optical fiber ensures excellent transmission performance. (Unlike non-standard or junk fiber, the attenuation of the fiber increases, which may lead to no light in the later stage. Because the roundness of this fiber is not enough, the mode field diameter is unstable, and the attenuation will be very large at the 1550 window after pulling, As a result, the business cannot be opened, and the optical fiber is seriously broken. For example: 9-125 single-mode G652D optical fiber
3. Loose tube: PBT material, hard and flexible, resistant to lateral compression and tension, and good mechanical properties.
4. Aramid yarn: imported aramid yarn (national aramid yarn and imported aramid yarn cannot be seen on the surface, but the difference can be clearly detected after testing: national spinning yarn, the tensile strength is reduced by half. When the whole cable is stressed At 2000N, the A-grade optical fiber is stretched within 3%, which will not affect the normal use of the optical cable. The stretching of the national spinning yarn or other yarn will reach 7%-8%, which will cause the optical cable index attenuation to not recover or the optical fiber to break. .)
5. Sheath: PE sheath imported from northern Europe (bad sheath material may cause cracks after use, which cannot protect the bundled fiber)
ADSS manufacturer’s layer-twisted structure products adopt “SZ” bidirectional layer-twisting technology. The important thing is that the pitch design is reasonable to ensure that there are enough windows, and the amount of aramid yarn and the perfect stranding process are carefully designed to meet the application requirements of different spans and environments.
Production process description: (four processes)
1. Optical fiber coloring process:
Colored fiber color does not migrate and does not fade
· The fiber optic cable is neat and flat, not chaotic, and not crimped
The fiber attenuation index meets the requirements
2. Two sets of optical fiber technology:
·Fiber excess length control
·Loose tube outer diameter and wall thickness control
· The fullness of the ointment in the tube
· For the color separation beam tube, the color should be bright and consistent, and it is easy to separate colors
3. Cable forming process:
·Cable pitch
·Binding pitch, yarn binding tension
·Pay-off and take-up tension
4. Sheathing process:
Reasonable gap between steel, aluminum tape and cable core
·The lap width of the steel-aluminum strip meets the requirements
·Sheath thickness meets process requirements
·The printing is clear and complete, and the meter mark is accurate
· The wiring is neat and flat
Post time: Aug-03-2022